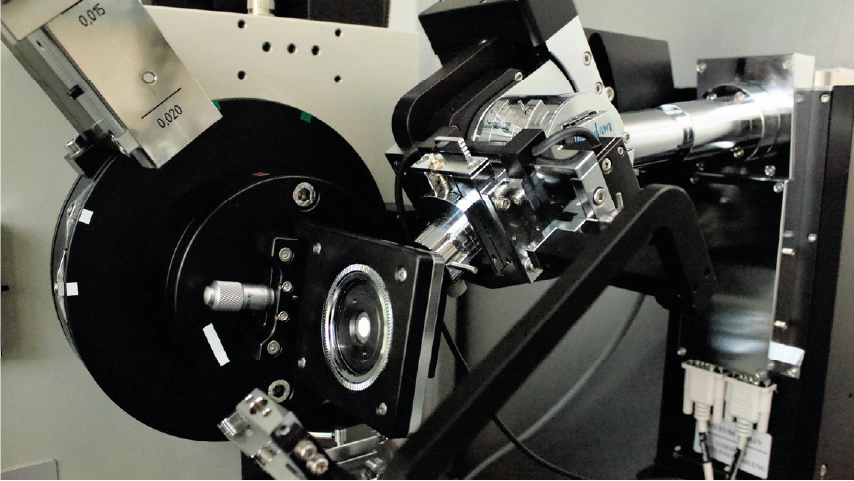
Mineralogie-/Biogeochemie-Geräte
Kontakt:
Web:
Infrastrukturzugehörigkeit:
Die Labore für Umweltmineralogie und Biogeochemie sind mit einer Vielzahl spektroskopischer und streuungsbasierter Messgeräte ausgestattet, um die chemische Zusammensetzung, Struktur, Oberfläche und Korngröße sowohl synthetischer als auch natürlicher Proben zu bestimmen. Zum Beispiel,
-
Unser Pulver-Röntgendiffraktometer (XRD) besteht aus zwei Einzelgeräten, die Röntgenstreuungsanalysen sowohl mit Cu- (λ=1.54 Å) als auch mit Ag-Strahlung (λ=0.56 Å) in Transmissionsgeometrie durchführen können. Mit XRD können sowohl kristalline als auch amorphe Proben analysiert werden, indem entweder konventionelle Beugungsmuster oder Totalstreuungsmuster mit hohem Q-Bereich zur Analyse der Paarverteilungsfunktion (PDF) gemessen werden. Die Messungen können bei Raum- oder erhöhter Temperatur bis zu 800 ⁰C durchgeführt werden.
-
Das IR-Spektrometer dient zur schnellen Routine-IR-Spektrenaufnahme im Bereich 4000-400 cm⁻¹ mit einer maximalen Auflösung von 0,9 cm⁻¹, obwohl in der Praxis selten eine höhere Auflösung als 4 cm⁻¹ erforderlich ist. IR-Spektren können sowohl an flüssigen als auch an festen Proben gemessen werden.
-
Das UV-Vis-Spektralphotometer (UV/VIS) misst die Absorption von Licht im Bereich von 190-1100 nm. Die Messungen sind entweder im ex-situ-Modus in Küvetten oder in-situ mit einer externen Sonde möglich. Das Gerät wird hauptsächlich für die Bestimmung von Elementkonzentrationen (z.B. Fe²⁺, As, Si, P) mittels etablierter kolorimetrischer Methoden eingesetzt. Darüber hinaus kann das Spektralphotometer auch für die In-situ- und Echtzeit-Überwachung der Keimbildung, Kristallisation und des Wachstums von Mineralien verwendet werden und ist mit einem Einzelzellen-Peltier-System für die Temperaturregelung und das Probenrühren ausgestattet.
Fachspezifische Schlagworte
- Differential Scanning Calorimetry
- X-Ray Powder Diffraction
- Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
- Particle Analysis
- Optical Microscopy
- UV-VIS Spectrophotometry
- Photometry
- Microscopy
- Surface Area Analysis
- Zeta-Potential Measurement
- Differential Thermal Analysis
- Thermogravimetric Analysis
- Biogeochemie
- Geochemie
- Mineralogie
Kategorien
Instrumentierung
Laboratory instrumentation
Instrumente
-
Zeta-Potential Analyzer
-
Surface Area Analyzer
-
Particle Analyzer
-
Optical Microscope
-
UV-VIS Spectrophotometer
-
Thermal Analysis Platform
-
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometer
FTIR Spectrometer - Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometer
Traditional (dispersive) infrared techniques experience difficulties due to the '1 wavenumber at a time' nature of data acquisition. This leads to either a poor signal to noise ratio in a spectrum or a very long time needed to obtain a high quality spectrum. Both these situations cause problems with kinetic work. The first gives inherent large errors, the second prohibits in-situ work. These problems can be overcome using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) that is based on the interferometer originally designed by Michelson and a mathematical procedure developed by Fourier that converts response from the 'time' to the 'frequency' domain.
In the Michelson interferometer a parallel, polychromatic beam of radiation from a source (A) is directed to a beam splitter (B), made from an infrared transparent material, such as KBr. The beam splitter reflects approximately half of the light to a mirror, known as the fixed mirror (C), which in turn reflects the light back to the beam splitter. The rest of the light passes through to a mirror, moving continuously, at a known velocity, back and forth along the direction of the incoming light and this is known as the moving mirror (D). Upon reflection from the moving mirror, radiation is then directed back to the beam splitter. At the beam splitter some of the light that has been reflected from the fixed mirror combines with light reflected from the moving mirror and is directed towards the sample. After passing through the sample (E) the radiation is focused onto the detector (F). The detectors are sufficiently fast to cope with time domain signal changes from the modulatio n in the interferometer. Additional information available at http://physics.nist.gov/Divisions/Div842/Gp1/fts_intro.html (Source: Global Change Master Directory (GCMD). 2023. GCMD Keywords, Version 16.3. Greenbelt, MD: Earth Science Data and Information System, Earth Science Projects pision, Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). URL (GCMD Keyword Forum Page): https://forum.earthdata.nasa.gov/app.php/tag/GCMD+Keywords)
-
Photometer
Photometers are instruments used for measuring the luminance, luminous intensity, or luminance of a light source; similar to a radiometer, but with an output weighted by the wavelength response of the human eye. (Source: Global Change Master Directory (GCMD). 2023. GCMD Keywords, Version 16.3. Greenbelt, MD: Earth Science Data and Information System, Earth Science Projects pision, Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). URL (GCMD Keyword Forum Page): https://forum.earthdata.nasa.gov/app.php/tag/GCMD+Keywords)
-
X-Ray Powder Diffractometer
An x-ray powder diffractometer is primarily used for the identification of phases in powder form. An x-ray beam of known wavelength is focused on a powdered sample and x-ray diffraction peaks are measured using a germanium detector; the d-spacing of the observed diffraction peaks is calculated using Bragg's Law [n*lamda = 2dsin(theta)]. The Scintag Pad V automated powder diffractometer uses a Cu x-ray tube with variable filters, a four-sample changer, and a low-noise, high efficiency, liquid-nitrogen cooled germanium detector. The goniometer is automated and software packages are run from a PC running Windows NT 4. A number of Scintag software packages are available for routine powder diffraction data acquisition, background correction and peak identification. Unknowns can be matched to JCPDS cards in an on-line database. Other software is available for quantitative analysis of powder mixtures, unit cell refinement, Rietveld analysis, and GSAS structural analysis. Samples sho uld be prepared as powders with a grain size of 10 um (approximately), and typically about 100 milligrams of sample is required. Additional information available at "http://www.gps.caltech.edu/facilities/analytical/xrd.html" [Summary provided by Caltech] (Source: Global Change Master Directory (GCMD). 2023. GCMD Keywords, Version 16.3. Greenbelt, MD: Earth Science Data and Information System, Earth Science Projects pision, Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). URL (GCMD Keyword Forum Page): https://forum.earthdata.nasa.gov/app.php/tag/GCMD+Keywords)
Beziehungen
- ist Teil von
- steht in Zusammenhang mit